

























[1] 中华人民共和国农业农村部. 2019. 全国农业植物检疫性有害生物分布行政区名录(2019). (农办农〔2019〕12号).
[2] 中华人民共和国农业农村部. 2018. 全国农业植物检疫性有害生物分布行政区名录(2018). (农办农〔2018〕10号). 索引号: 07B100414201800362.
[3] 张玮, 刘桂林, 钟平生, 周善义. 2014. 罗浮山景区蚁科昆虫调查. 惠州学院学报. 34(3): 46-50.
[4] 冉浩. 2014. 蚂蚁之美. 北京: 清华大学出版社.
[5] 赵爽, 贾凤龙, 梁铬球, 柯云玲, 田伟金. 2009. 广东省蚂蚁种类与分布. 环境昆虫学报. 31(2): 156-161.
[6] 黄建华, 周善义. 2007. 中国蚁科昆虫名录——切叶蚁亚科(Ⅲ). 广西师范大学(自然科学版). 25(3): 88-96.
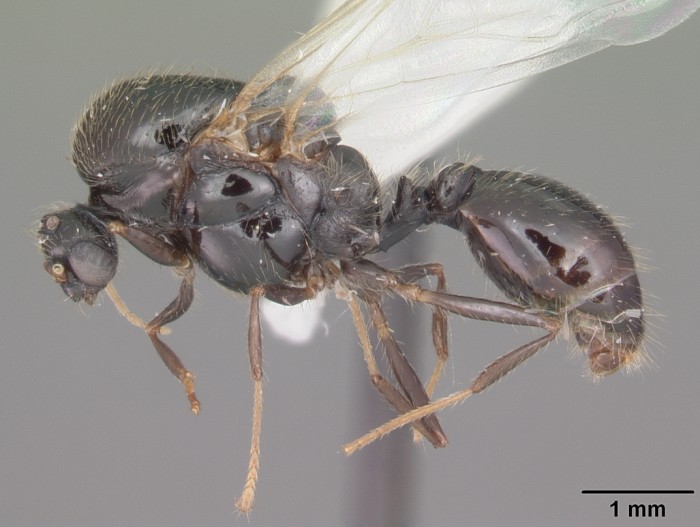
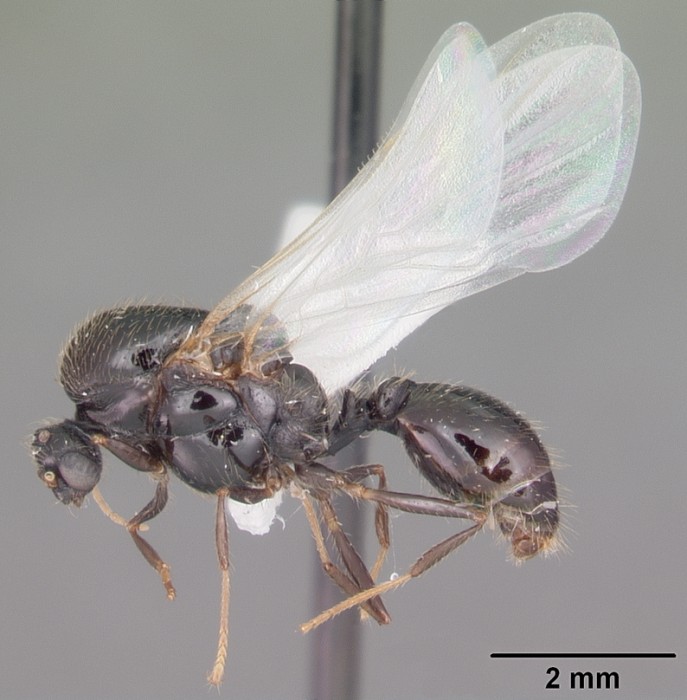
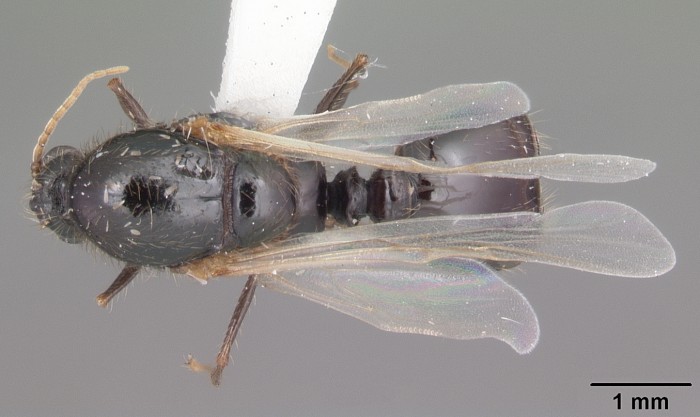
[7] 陈乃中, 施宗伟, 马晓光. 2005. 红火蚁及其重要近似种的鉴别. 昆虫知识. 42(3): 341-345.
[8] Roeder, K. A., D. V. Roeder, and M. Kaspari. 2018. The role of temperature in competition and persistence of an invaded ant assemblage. Ecological Entomology. 43:774-781.
[9] Pitts, J.P., Camacho, G.P., Gotzek, D., McHugh, J.V., Ross, K.G. 2018. Revision of the fire ants of the Solenopisis saevissima species group (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Proceedings of the Entomological Society of Washington, 120: 308–411.
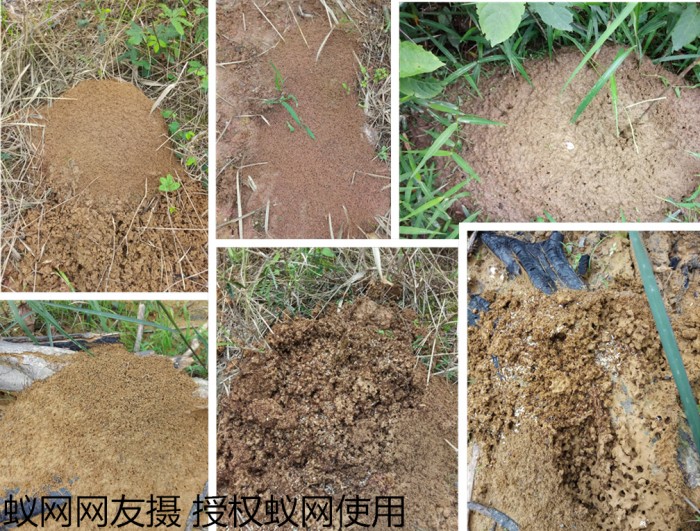
[10] Tschinkel, W.R. 2015. The architecture of subterranean ant nests: beauty and mystery underfoot. Journal of Bioeconomics 17:271–291.
[11] Palomeque, T., O. Sanllorente, X. Maside, J. Vela, P. Mora, M. I. Torres, G. Periquet, and P. Lorite. 2015. Evolutionary history of the Azteca-like mariner transposons and their host ants. Science of Nature. 102.
[12] Wetterer, J. K. 2013. Exotic spread of Solenopsis invicta Buren (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) beyond North America. Sociobiology 60:50-55.
[13] Lei, W., Yongyue, L.U., Yijuan, X.U. & Ling, Z. 2013. The current status of research on Solenopsis invicta Buren (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in Mainland China. Asian Myrmecology 5, 125–137.
[14] Yongsheng Gao, Fabian Bracco, Sanqiang Zhao, Terrence Michael Caelli. 2012. An Automatic On-Site Fire Ant Screening System. IEEE Computer Society.
[15] Espadaler, X., Santamaria, S. 2012. Ecto- and Endoparasitic Fungi on Ants from the Holarctic Region. Psyche Article ID 168478, 10 pages.
[16] Wurm, Y. et al. 2011. The genome of the fire ant Solenopsis invicta. PNAS. 108(14):5679-5684.
[17] Ward, D. 2009. The potential distribution of the red imported fire ant, Solenopsis invicta Buren (Hymenoptera: Formicidae), in New Zealand. New Zealand Entomologist 32: 67-75.
[18] Shattuck, S. O.; Porter, S. D.; Wojcik, D. P. 2004. Case 3069. Solenopsis invicta Buren, 1972 (Insecta, Hymenoptera): proposed conservation of the specific name. Bull. Zool. Nomencl. 56: 27-30.
[19] Deyrup, M., Davis, L. & Cover, S. 2000. Exotic ants in Florida. Transactions of the American Entomological Society 126, 293-325.
[20] Trager, J. C. 1991. A revision of the fire ants, Solenopsis geminata group (Hymenoptera: Formicidae: Myrmicinae). J. N. Y. Entomol. Soc. 99: 141-198.
[21] Smith, D. R. 1979. Superfamily Formicoidea. Pp. 1323-1467 in: Krombein, K. V., Hurd, P. D., Smith, D. R., Burks, B. D. (eds.) Catalog of Hymenoptera in America north of Mexico. Volume 2. Apocrita (Aculeata). Washington, D.C.: Smithsonian Institution Pr.
[22] Wheeler, G. C.; Wheeler, J. 1977a. Supplementary studies on ant larvae: Myrmicinae. Trans. Am. Entomol. Soc. 103: 581-602.
[23] Buren, W. F. 1972. Revisionary studies on the taxonomy of the imported fire ants. J. Ga. Entomol. Soc. 7: 1-26.